2024 Full Moon calendar: Dates, times, types, and names
For millennia, Full Moons have wielded a magnetic charm. This monthly event has been the inspiration behind myths, tales, traditions, and even farming. We’ll update this article multiple times each week with the latest moonrise, moonset, Full Moon schedule, and what you can see in the sky each week.
The Full Moon in February 2024 is at 7:30 a.m. on Saturday, Feb. 24.
Here’s the complete list of Full Moons in 2024 along with their traditional names

2024 Full Moon schedule
(all times Eastern)
Jan. 25 — 12:54 p.m. — Wolf Moon Feb. 24 —7:30 a.m. — Snow Moon March 25 — 3 a.m. — Worm Moon April 23 — 7:49 p.m. — Pink Moon May 23 — 9:53 a.m. — Flower Moon June 21 — 9:08 p.m. — Strawberry Moon July 21 — 6:17 a.m. — Buck Moon Aug. 19 — 2:26 p.m. — Sturgeon Moon Sept. 17 — 10:34 p.m. — Corn Moon Oct. 17 — 7:26 a.m. — Hunter’s Moon Nov. 15 — 4:28 p.m. — Beaver Moon Dec. 15 — 4:02 a.m. Cold Moon The phases of the Moon in January 2024
These images below show the day-by-day phases of the moon this month. The next Full Moon is at 12:54 p.m. ET on Thursday, Jan. 25.
The moonrise and moonset schedule this week
The following is adapted from Alison Klesman’s The Sky This Week article, which you can find here.
Sunday, January 28
Sunrise: 7:12 A.M.Sunset: 5:14 P.M.Moonrise: 8:11 P.M.Moonset: 8:57 A.M.Moon Phase: Waning gibbous (92%)
Monday, January 29
The Moon reaches apogee, the farthest point from Earth in its orbit, at 3:14 A.M. EST. At that time, it will sit 252,138 miles (405,777 km) away.
Sunrise: 7:12 A.M.Sunset: 5:15 P.M.Moonrise: 9:11 P.M.Moonset: 9:17 A.M.Moon Phase: Waning gibbous (86%)
Tuesday, January 30
Sunrise: 7:11 A.M.Sunset: 5:16 P.M.Moonrise: 10:09 P.M.Moonset: 9:37 A.M.Moon Phase: Waning gibbous (79%)
Wednesday, January 31
Sunrise: 7:10 A.M.Sunset: 5:18 P.M.Moonrise: 11:10 P.M.Moonset: 9:56 A.M.Moon Phase: Waning gibbous (71%)
Thursday, February 1
Sunrise: 7:09 A.M.Sunset: 5:19 P.M.Moonrise: —Moonset: 10:16 A.M.Moon Phase: Waning gibbous (62%)
Friday, February 2Last Quarter Moon occurs at 6:18 P.M. EST. This lunar phase often goes unnoticed because the Moon is most prominent in the predawn sky. But it’s also a unique and lovely phase, as the light “reverses” across the Moon’s surface with the setting Sun. (You can think of First Quarter as sunrise on the Moon, Full Moon as high noon, and Last Quarter as sunset. So, shadows that stretched in one direction during First Quarter now stretch the other during Last Quarter.)
A few hours before dawn, the Moon floats high in the south in southeastern Virgo. This is a lovely region of sky with several interesting stars. In addition to enjoying the lunar surface through your telescope, look also 13.5° to our satellite’s northwest (upper right) to land on Spica, Virgo’s bright, blue-white alpha star. From here, continue nearly the same distance — 14.5° — farther to find Porrima, cataloged as Gamma (γ) Virginis and well known as a lovely double star. Both components are roughly the same magnitude and lie a mere 3″ apart.
Sunrise: 7:08 A.M.Sunset: 5:20 P.M.Moonrise: 12:11 A.M.Moonset: 10:40 A.M.Moon Phase: Waning gibbous (52%)
How and why do Full Moons occur?
The phenomenon of a Full Moon arises when our planet, Earth, is precisely sandwiched between the Sun and the Moon. This unique alignment ensures the entire side of the Moon that faces us gleams under sunlight. And thanks to the Moon’s orbit around Earth, the angle of sunlight hitting the lunar surface and being reflected back to our planet evolves, giving birth to varied lunar phases.
These phases span the New Moon, waxing crescent, First Quarter, waxing gibbous, Full Moon, waning gibbous, Last Quarter, and waning crescent. A cycle starting from one Full Moon to its next counterpart, termed the synodic month or lunar month, lasts about 29.5 days.
Though a Full Moon only occurs during the exact moment when Earth, Moon, and Sun form a perfect alignment, to our eyes, the Moon seems Full for around three days.
Different names for different types of Full Moon
There are a wide variety of specialized names used to identify distinct types or timings of Full Moons. These names primarily trace back to a blend of cultural, agricultural, and natural observations about the Moon, aimed at allowing humans to not only predict seasonal changes, but also track the passage of time.
For instance, almost every month’s Full Moon boasts a name sourced from Native American, Colonial American, or other North American traditions, with their titles mirroring seasonal shifts and nature’s events.
A composite of each month’s Full Moon in 2020. Credit: Soumyadeep Mukherjee
Wolf Moon (January): Inspired by the cries of hungry wolves.
Snow Moon (February): A nod to the month’s often heavy snowfall.
Worm Moon (March): Named after the earthworms that signal thawing grounds.
Pink Moon (April): In honor of the blossoming pink wildflowers.
Related: How to see the eclipse in April
Flower Moon (May): Celebrating the bloom of flowers.
Strawberry Moon (June): Marks the prime strawberry harvest season.
Buck Moon (July): Recognizing the new antlers on bucks.
Sturgeon Moon (August): Named after the abundant sturgeon fish.
Corn Moon (September): Signifying the corn harvesting period.
Hunter’s Moon (October): Commemorating the hunting season preceding winter.
Beaver Moon (November): Reflects the time when beavers are busy building their winter dams.
Cold Moon (December): Evocative of winter’s chill.
In addition, there are a few additional names for Full Moons that commonly make their way into public conversations and news.
Super Moon: This term is reserved for a Full Moon that aligns with the lunar perigee, which is the Moon’s nearest point to Earth in its orbit. This proximity renders the Full Moon unusually large and luminous. For a Full Moon to earn the Super Moon tag, it should be within approximately 90 percent of its closest distance to Earth.
Blue Moon: A Blue Moon is the second Full Moon in a month that experiences two Full Moons. This phenomenon graces our skies roughly every 2.7 years. Though the term suggests a color, Blue Moons aren’t truly blue. Very occasionally, atmospheric conditions such as recent volcanic eruptions might lend the Moon a slightly blueish tint, but this hue isn’t tied to the term.
Harvest Moon: Occurring closest to the autumnal equinox, typically in September, the Harvest Moon is often renowned for a distinct orange tint it might display. This Full Moon rises close to sunset and sets near sunrise, providing extended hours of bright moonlight. Historically, this was invaluable to farmers gathering their produce.
Common questions about Full Moons Moonrise over the Syr Darya river in Baikonur, Kazakhstan on Nov. 13, 2016. Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
What is the difference between a Full Moon and a New Moon? A Full Moon is witnessed when Earth lies between the Sun and the Moon, making the entire Moon’s face visible. Conversely, during a New Moon, the Moon lies between Earth and the Sun, shrouding its Earth-facing side in darkness.
How does the Full Moon influence tides? The Moon’s gravitational tug causes Earth’s waters to bulge, birthing tides. During both Full and New Moons, the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in alignment, generating “spring tides.” These tides can swing exceptionally high or low due to the combined gravitational influences of the Sun and Moon.
Do Full Moons have an impact on human behavior? While numerous tales suggest Full Moons stir human behavior, causing increased restlessness or even lunacy, rigorous scientific analyses have largely debunked these tales.
Full Moons, in their myriad forms, stand testament to humanity’s enduring captivation with the cosmos. They evoke not just our celestial connection but also tether us to Earth’s rhythms. Whether you’re an avid stargazer or an occasional night sky admirer, Full Moons invariably call for our attention, inviting both introspection and marvel.
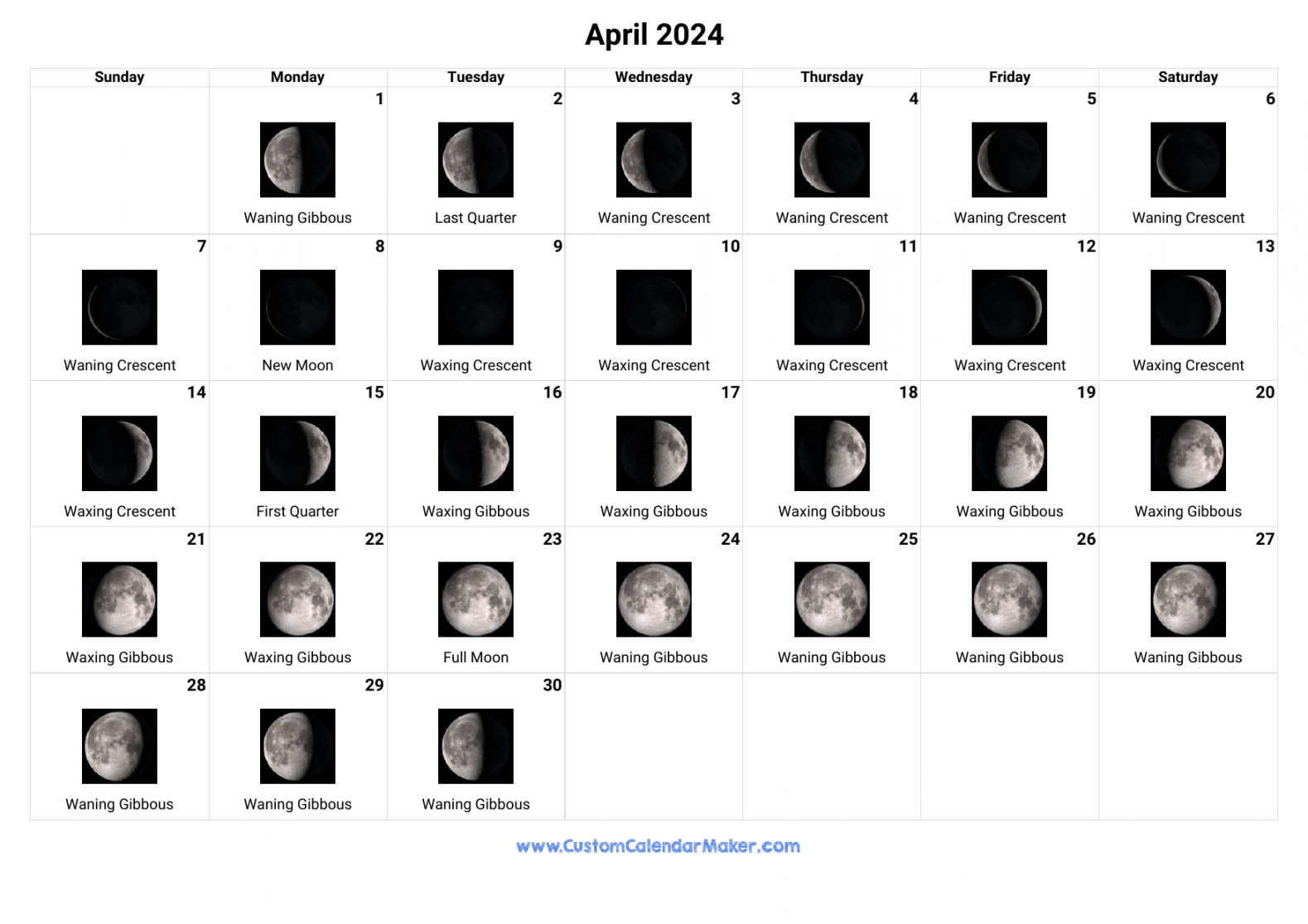
Here are the dates for all the lunar phases in 2024:
New First Quarter Full Last Quarter Jan. 3 Jan. 11 Jan. 17 Jan. 25 Feb. 2 Feb. 9 Feb. 16 Feb. 24 March 3 March 10 March 17 March 25 April 1 April 8 April 15 April 23 May 1 May 7 May 15 May 23 May 30 June 6 June 14 June 21 June 28 July 5 July 13 July 21 July 27 Aug. 4 Aug. 12 Aug. 19 Aug 26 Sept. 2 Sept. 11 Sept. 17 Sept. 24 Oct. 2 Oct. 10 Oct. 17 Oct. 24 Nov. 1 Nov. 9 Nov. 15 Nov. 22 Dec. 1 Dec. 8 Dec. 15 Dec. 22 Dec. 30